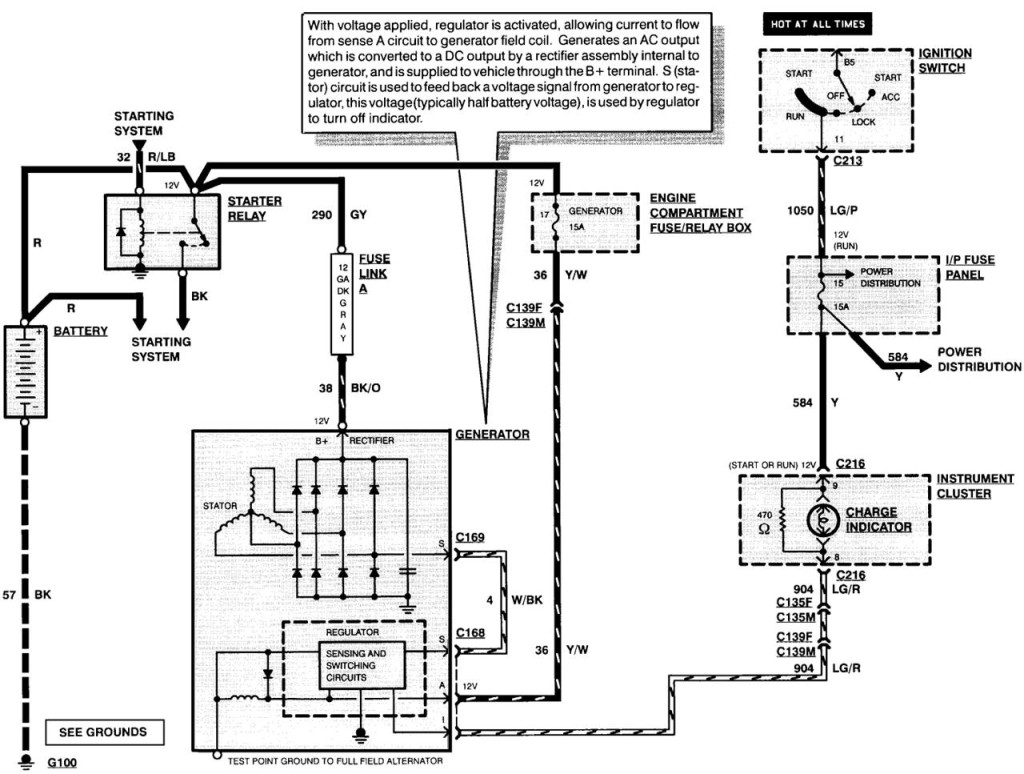
When it comes to understanding the electrical system in your Ford vehicle, the Ford Alternator Wiring Schematic is a crucial component. This schematic provides a detailed diagram of the wiring layout for the alternator in your Ford vehicle, allowing you to easily identify and troubleshoot any electrical issues that may arise.
Why are Ford Alternator Wiring Schematics essential?
The Ford Alternator Wiring Schematic is essential for several reasons:
- It provides a visual representation of the wiring connections for the alternator, making it easier to understand how the electrical system functions.
- It helps in diagnosing and troubleshooting any issues with the alternator or related components.
- It assists in proper installation or replacement of the alternator, ensuring correct wiring connections are made.
How to read and interpret Ford Alternator Wiring Schematics effectively
Reading and interpreting a Ford Alternator Wiring Schematic may seem daunting at first, but with a little guidance, it can be a valuable tool:
- Start by familiarizing yourself with the symbols and color codes used in the schematic.
- Follow the wiring paths to understand how the electrical current flows through the alternator system.
- Identify the different components connected to the alternator and their respective wiring connections.
Using Ford Alternator Wiring Schematics for troubleshooting electrical problems
When faced with electrical issues in your Ford vehicle, the Ford Alternator Wiring Schematic can be a lifesaver:
- Use the schematic to trace the wiring connections and identify any loose or damaged wires that may be causing the problem.
- Check for proper voltage levels at various points in the alternator system to pinpoint the source of the issue.
- Refer to the schematic to ensure that all wiring connections are correct and secure.
Safety tips and best practices
Working with electrical systems and wiring diagrams can be hazardous if proper precautions are not taken. Here are some safety tips to keep in mind:
- Always disconnect the battery before working on any electrical components to prevent the risk of electric shock.
- Use insulated tools and wear protective gear, such as gloves and goggles, when handling electrical components.
- Double-check all wiring connections before reassembling any components to avoid short circuits or other electrical hazards.
Ford Alternator Wiring Schematic
3 Wire Ford Alternator Wiring Diagram

Ford F150 Alternator Wiring Diagram

Understanding the Ford Alternator Wiring Schematic: A Step-by-Step Guide

Ford Alternator Wiring

Ford Alternator Wiring Diagram – Wiring Diagram

Ford alternator wiring diagram internal regulator